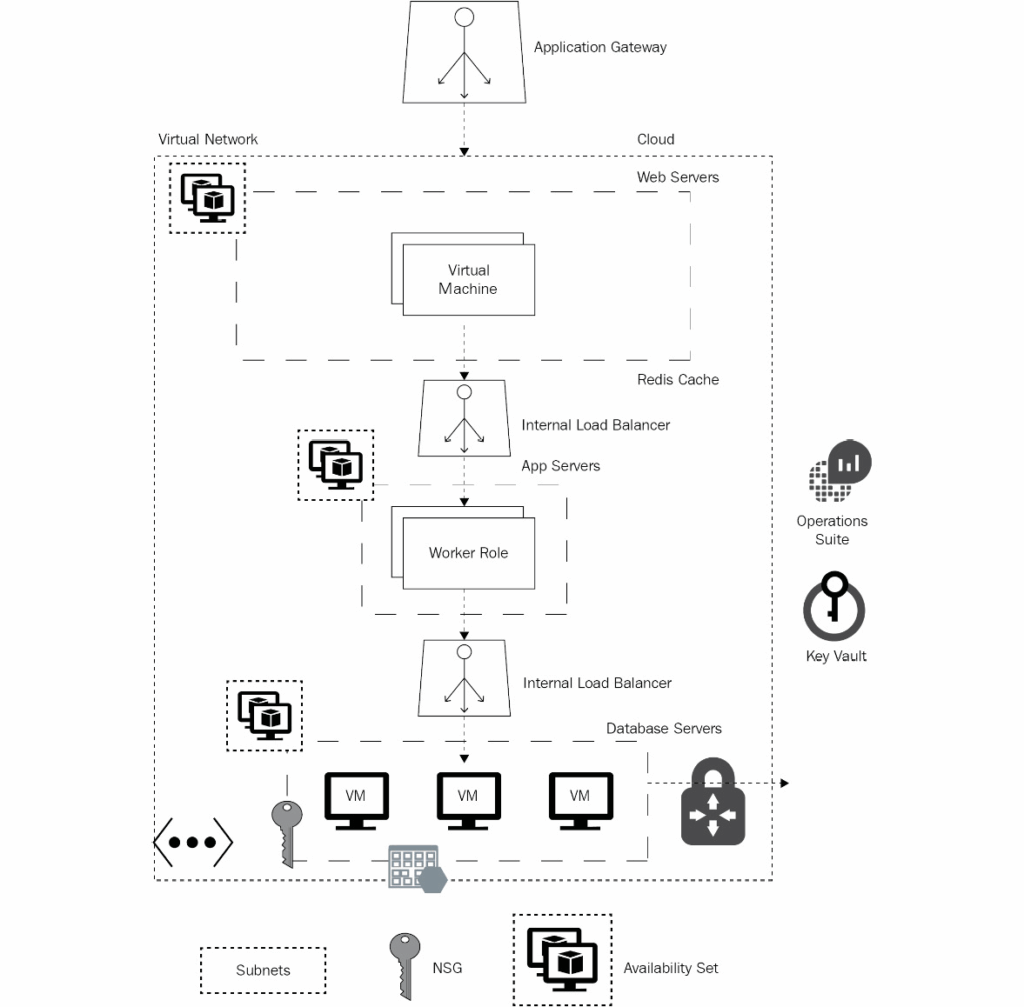
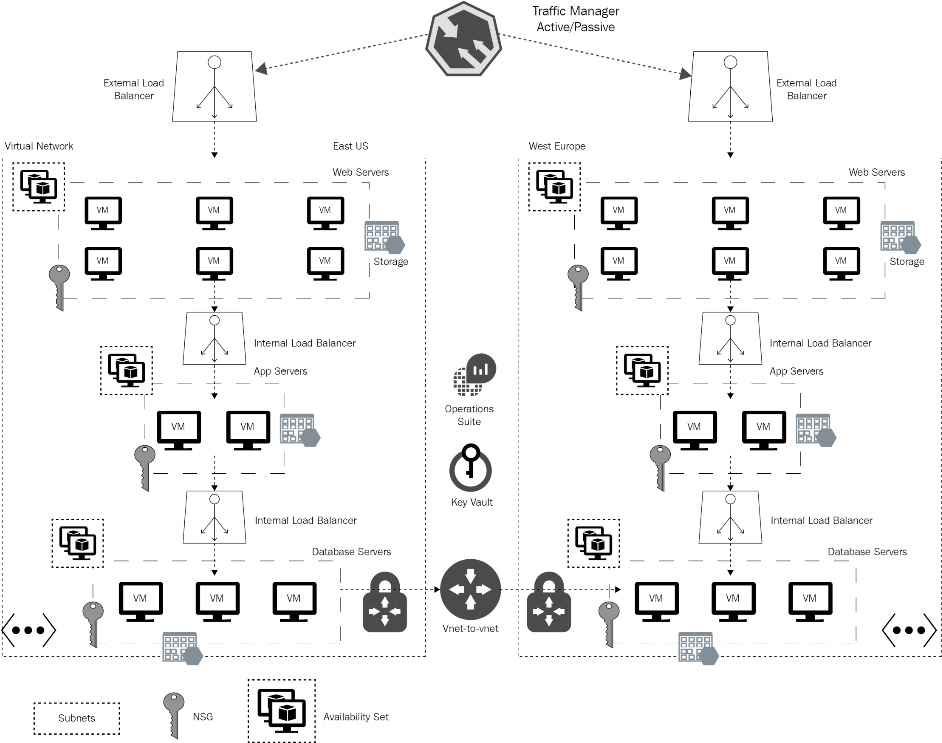
Availability sets:
A minimum of two VMs should be hosted within the availability set to make them highly available. All VMs in the availability set become highly available because they are placed on separate physical racks in the Azure datacenter. During updates, these VMs are updated one at a time, instead of all at the same time. Availability sets provide a fault domain and an update domain to achieve this.
In short, availability sets provide redundancy at the datacenter level
Availability zones:
Availability zones provide high availability within a region by placing VM instances on separate datacenters within the region. Availability zones are applicable to many resources in Azure, including VMs, managed disks, VM scale sets, and load balancers
Zone-redundant services replicate your applications and data across availability zones to protect from single points of failure.
Azure tries to make even single VM instances highly available for 99.9% of the time, particularly if these single-instance VMs use premium storage for their disks. Azure provides a higher SLA for those VMs that are grouped together in an availability set. It provides a 99.95% SLA for VMs that are part of an availability set with two or more VMs. The SLA is 99.99% if VMs are placed in availability zones.
While Service Fabric allows any type of application to become highly available, orchestrators such as Kubernetes, DC/OS, and Swarm are specific to containers.