Virtual Network Address Translation (NAT) is a feature of a VNet that allows outbound internet communication from VMs and other resources connected to the VNet. When you enable NAT, the VNet assigns a public IP address to the VM or resource, which can then communicate with the internet using that IP address.
Azure NAT is a feature that enables outbound-only internet connectivity for VMs in an Azure virtual network. NAT allows VMs to connect to the internet but the internet cannot initiate connections to the VMs. Azure NAT can be configured using Azure NAT Gateway, a fully managed Azure service that provides outbound-only internet connectivity for VMs in a virtual network.
The Azure NAT feature is helpful in scenarios where you want to allow outbound internet communication from your VNet. Still, you don’t want the resources to be directly accessible from the internet. For example, you can use Azure NAT if you have a VM that needs to download updates from the internet but don’t want to expose the VM to the internet.
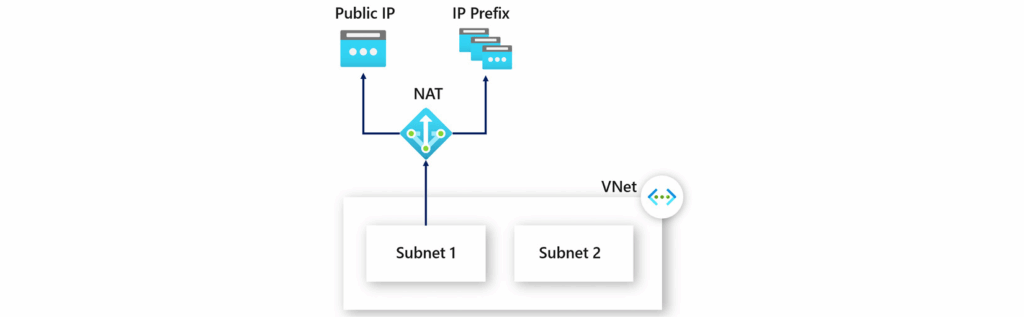
The following figure shows the outbound traffic flow from Subnet 1 through the NAT gateway, which is mapped to a public IP address or a public IP prefix.